Mastering Active Transitive Verbs in Indonesian

Have you ever struggled to express yourself clearly and concisely in Indonesian? The key to unlocking fluent and impactful communication might lie in understanding a fundamental grammatical concept: active transitive verbs, or kata kerja aktif transitif. These verbs are the backbone of dynamic sentences, allowing you to paint vivid pictures with your words and convey your message effectively.
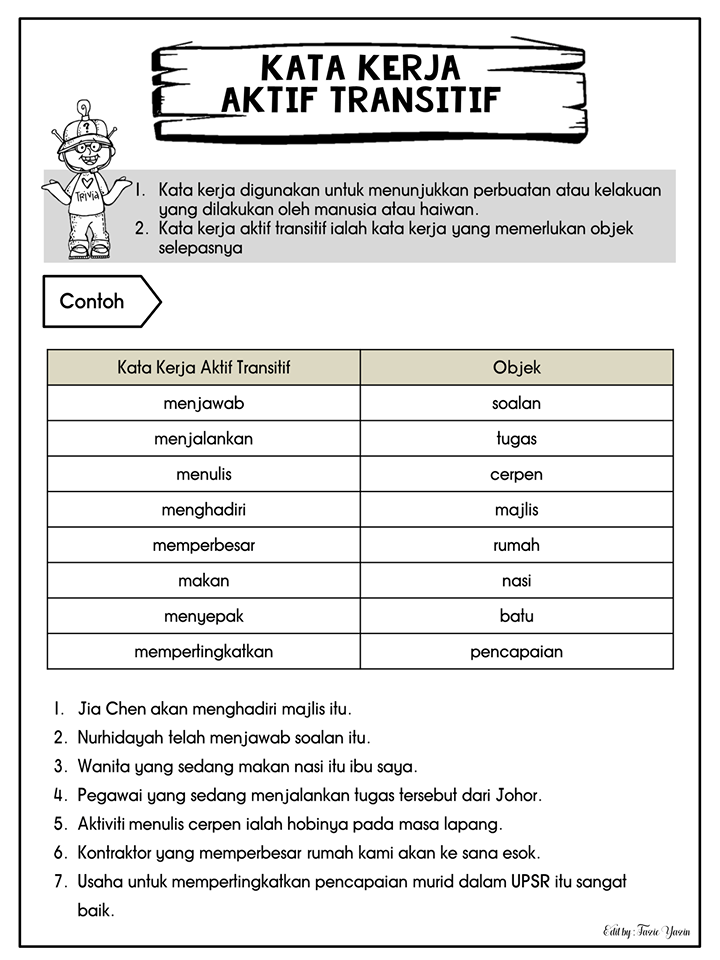
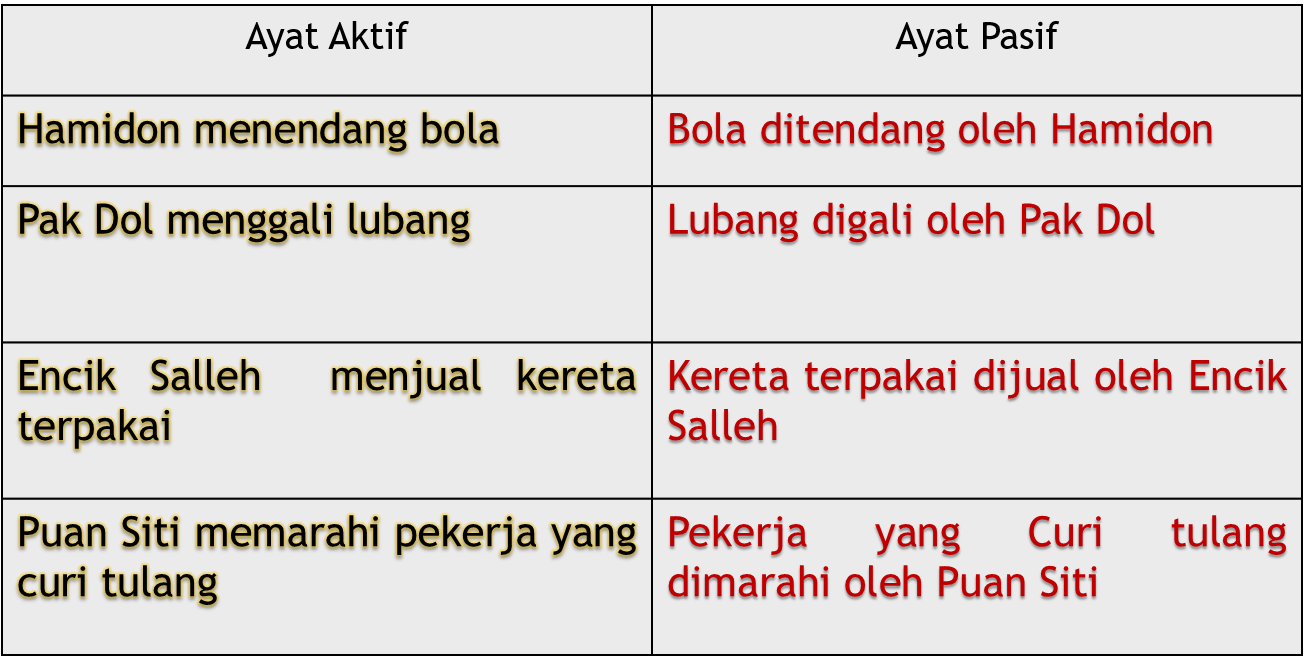
Contoh kata kerja aktif transitif translates to "examples of active transitive verbs." These verbs are action words that require a direct object to complete their meaning. Unlike intransitive verbs, which stand alone, transitive verbs need a recipient of the action. Think of it like throwing a ball – you throw (the verb) the ball (the object). Without the ball, the action of throwing is incomplete. Mastering these verbs is crucial for anyone wanting to achieve fluency in Indonesian.
While the exact origin and historical development of transitive verbs in Indonesian grammar is complex and intertwined with the evolution of the language itself, their importance is undeniable. They form the foundation of sentence structure and allow for nuanced expression. By understanding how these verbs function, you gain a deeper understanding of the language's mechanics and can construct more sophisticated sentences.
One of the main issues learners face with kata kerja aktif transitif is identifying them correctly. Indonesian, unlike English, doesn't always rely on word order to determine the object. Context and prefixes/suffixes on the verb often play a crucial role. This requires careful attention to sentence structure and a good grasp of Indonesian vocabulary.
Simply put, a kata kerja aktif transitif is a verb that takes a direct object. For example, "membaca" (to read) is a transitive verb. You read something. "Saya membaca buku" (I read a book). "Buku" (book) is the direct object, receiving the action of reading. Other examples include "menulis" (to write), "memakan" (to eat), and "meminum" (to drink).
One benefit of using active transitive verbs is clarity. They create direct and concise sentences, leaving no room for ambiguity. Another benefit is that they make your writing more dynamic and engaging. Active voice, which often utilizes transitive verbs, is generally preferred in writing as it creates a stronger impact on the reader. Finally, understanding these verbs allows you to grasp the nuances of Indonesian grammar and appreciate the richness of the language.
To master active transitive verbs, start by learning common examples. Practice constructing sentences with these verbs and varying the direct objects. Pay attention to how native speakers use these verbs in conversation and in written materials. Immersion and consistent practice are key.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Focusing Heavily on Transitive Verbs
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Clarity and conciseness in communication. | Can lead to oversimplification if intransitive verbs are neglected. |
| Creates dynamic and engaging writing. | May not be suitable for all communicative contexts. |
| Improves understanding of Indonesian grammar. | Requires a solid understanding of direct objects and their role. |
Five real-world examples of active transitive verbs in Indonesian sentences are: 1. Ibu memasak nasi (Mother cooks rice). 2. Ayah membeli mobil (Father buys a car). 3. Anak membaca buku (The child reads a book). 4. Kucing mengejar tikus (The cat chases the mouse). 5. Saya menulis surat (I write a letter).
A common challenge for learners is confusing transitive and intransitive verbs. The solution is to focus on identifying the direct object. Another challenge is recognizing the prefixes and suffixes that indicate transitivity. Regular practice with different verb forms can help overcome this.
FAQ: 1. What is a transitive verb? 2. How do I identify a transitive verb in Indonesian? 3. What is the difference between a transitive and intransitive verb? 4. Why are transitive verbs important? 5. How can I improve my understanding of transitive verbs? 6. What are some common examples of transitive verbs? 7. Can a verb be both transitive and intransitive? 8. How do transitive verbs contribute to clear communication? (Answers would follow each question in a real article).
One tip for mastering kata kerja aktif transitif is to create flashcards with the verb on one side and an example sentence on the other. This helps you associate the verb with its usage in context.
In conclusion, understanding and effectively using kata kerja aktif transitif is essential for anyone learning Indonesian. These verbs are the building blocks of clear, concise, and engaging communication. While mastering them may present some challenges, the benefits of enhanced clarity, stronger writing, and a deeper understanding of Indonesian grammar make the effort worthwhile. By actively practicing and immersing yourself in the language, you can unlock the power of active transitive verbs and significantly improve your Indonesian language skills. Start incorporating these verbs into your daily practice today and witness the transformative impact they have on your ability to communicate effectively in Indonesian. Embrace the challenge, and the rewards of fluency will follow.
Exploring the paradox the most virtuous villain
Calumet county farms a land of opportunity
The rise of powerful women in manga